Seed Amplification Immunoassay (SAIA) for Synucleinopathies
Abstract
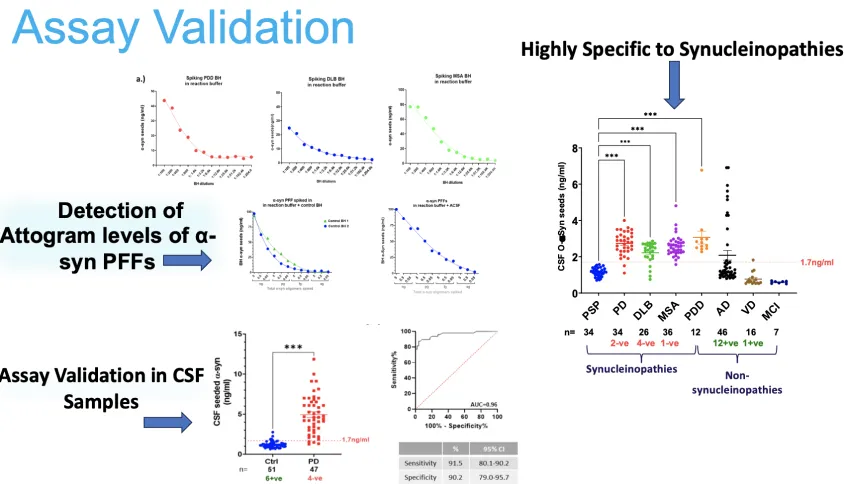
Synucleinopathies, including Parkinson’s disease (PD), dementia with Lewy bodies (DLB), and multiple system atrophy (MSA), are characterized by the accumulation of α-synuclein aggregates. Early and accurate diagnosis remains a critical challenge in managing these disorders. The Seed Amplification Immunoassay (SAIA) is a highly sensitive and specific diagnostic platform capable of detecting α-synuclein aggregates at attogram levels in various biofluids and tissue samples.
Our work on the SAIA highlights its remarkable utility in diagnosing synucleinopathies across diverse clinical and research applications. By leveraging its exceptional specificity, SAIA reliably differentiates synucleinopathies such as Parkinson’s disease, dementia with Lewy bodies, and multiple system atrophy from other neurodegenerative conditions.
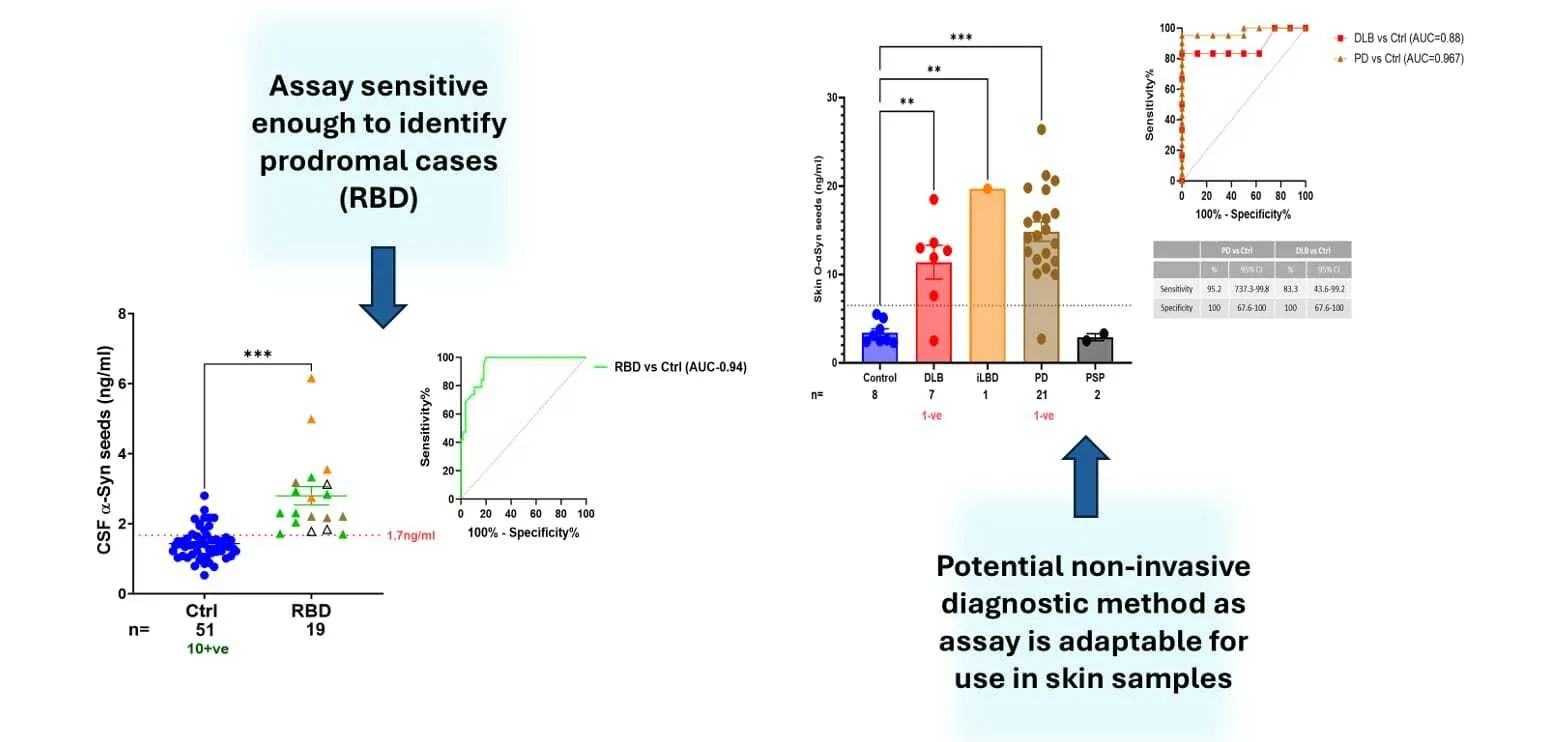
The assay’s high sensitivity enables the detection of α-synuclein aggregates at early stages of disease progression in cerebrospinal fluid and tissue samples, including brain and skin homogenates. Its application in prodromal cases, such as REM sleep behavior disorder (RBD), underscores its potential for identifying disease before the onset of motor symptoms. Furthermore, SAIA’s adaptability to skin biopsies expands its diagnostic versatility, offering a minimally invasive option for clinical settings.
These findings establish SAIA as a transformative tool for the early diagnosis and monitoring of synucleinopathies, paving the way for timely interventions and personalized therapeutic strategies to improve patient outcomes.
Key Performance Indicators
91.5%
Sensitivity
90.2%
Specificity
0.96
AUC
Conclusion
The SAIA assay represents a significant advancement in the diagnosis of synucleinopathies:
- High sensitivity and specificity for α-syn aggregates
- Early detection of trace amounts of aggregates in prodromal cases, supporting early diagnosis and timely intervention.
- Clear differentiation between synucleinopathies and other neurodegenerative disorders.
- Potential for monitoring disease progression and treatment efficacy in clinical trials.
These features position SAIA as a powerful tool in the fight against neurodegenerative diseases, offering new hope for early intervention and improved patient outcomes.